How Stormwater Management Revolutionizing Urban Water Sustainability
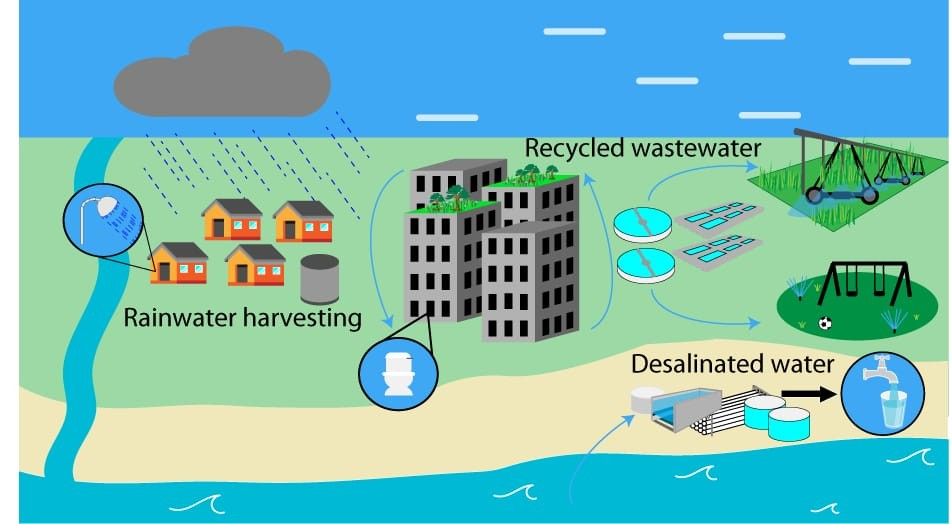
Stormwater management plays a crucial role in enhancing urban water sustainability by tackling challenges related to rapid urbanization and climate change. As cities expand, impervious surfaces such as roads and buildings prevent rainwater from naturally soaking into the ground. This leads to increased runoff, flooding, and water pollution.
Effective stormwater management solutions, such as green infrastructure, permeable pavements, and rain gardens, are revolutionizing how cities handle excess water while enhancing water quality, reducing flood risks, and replenishing groundwater. These innovative approaches not only improve water quality and reduce flood risks but also help replenish groundwater, thereby promoting ecological balance and urban resilience.
In this blog, we will explore how stormwater management is reshaping urban water sustainability and examine the cutting-edge techniques driving this transformation.
What is Stormwater Management?
Stormwater management refers to the process of controlling and treating rainwater runoff in urban and developed areas. It includes strategies such as storm drain concrete systems, green infrastructure, and porous surfaces designed to prevent flooding, reduce pollution, and manage water flow. The aim is to minimize the negative impacts of stormwater on
the environment while enhancing water sustainability by capturing, storing, or redirecting it for beneficial use.
8 Ways Stormwater Management Revolutionizing Urban Water Sustainability
- Reducing Water Pollution at the Source
One of the key ways that stormwater management is enhancing urban water sustainability is by focusing on reducing water pollution at the source. Traditional stormwater systems collect rainwater and runoff, which can carry pollutants such as oil, pesticides, and litter directly into water bodies.
By implementing innovative stormwater management practices, like green infrastructure and permeable pavements, cities can effectively capture and treat stormwater where it falls, preventing pollutants from entering waterways. This proactive approach not only reduces water pollution but also promotes a more sustainable and environmentally conscious urban water management system.
- Mitigating Urban Flooding
Mitigating urban flooding is a critical aspect of stormwater management that enhances urban water sustainability. Urban areas, with their high concentration of impervious surfaces, are particularly vulnerable to flooding during heavy rainfall events.
Effective stormwater management strategies, such as green infrastructure, permeable pavements, and retention ponds, can help reduce the impact of urban flooding by capturing and treating stormwater runoff before it overwhelms drainage systems. By integrating these innovative approaches into urban planning and development, cities can mitigate the risk of flooding and promote overall water sustainability for future generations.
- Promoting Groundwater Recharge
Promoting groundwater recharge is a key aspect of how stormwater management is revolutionizing urban water sustainability. By implementing strategies that allow stormwater to infiltrate the ground and replenish aquifers, cities can maintain healthy groundwater levels, which are vital for long-term water sustainability.
Techniques such as permeable pavements, green roofs, and rain gardens are increasingly utilized to capture and redirect stormwater, facilitating its absorption into the soil instead of allowing it to become runoff. This approach not only helps mitigate flooding and erosion but also plays a crucial role in enhancing urban resilience to the impacts of climate change on water resources.
- Enhancing Climate Resilience
Enhancing climate resilience through stormwater management is a vital aspect of improving urban water sustainability. As cities increasingly face challenges from extreme weather events due to climate change, effective stormwater management strategies are essential for mitigating flood risks and preserving water quality.
By implementing green infrastructure solutions such as permeable pavements, rain gardens, and green roofs, urban areas can minimize the impact of heavy rainfall and promote overall water sustainability. These innovative approaches help cities adapt to changing climate conditions, creating more resilient and environmentally friendly urban environments.
- Turning Stormwater into a Resource
Stormwater management plays a crucial role in revolutionizing urban water sustainability by turning stormwater into a valuable resource. Traditional stormwater systems often lead to excessive runoff, which can pollute waterways and strain existing infrastructure.
By adopting innovative stormwater management techniques like green infrastructure and rainwater harvesting, cities can capture and treat stormwater for reuse. This not only eases the burden on municipal water supplies but also reduces the risk of flooding and improves overall water quality in urban areas. Embracing these sustainable practices is essential for building more resilient and environmentally conscious cities in the future.
- Encouraging Community Involvement
Encouraging community involvement is a crucial aspect of revolutionizing urban water sustainability through stormwater management. By engaging residents, businesses, and organizations in the planning and implementation of stormwater management strategies, cities can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for their water resources.
Community participation can lead to greater awareness of the challenges posed by urban water issues and facilitate the development of innovative solutions tailored to each community’s specific needs. Furthermore, involving diverse stakeholders in the decision-making process can help build consensus and support for long-term sustainability initiatives.
- Lowering Infrastructure Costs
Stormwater management is critical in revolutionizing urban water sustainability by lowering infrastructure costs. Traditional methods often rely on expensive systems like underground pipes and storage tanks. In contrast, innovative approaches such as green infrastructure and permeable pavements provide more cost-effective solutions.
By adopting these sustainable practices, cities can alleviate the burden on existing infrastructure, lower maintenance costs, and build a more resilient urban water system. Investing in stormwater management not only benefits the environment but also offers a financially sustainable strategy for urban areas facing water-related challenges.
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Meeting regulatory requirements is a crucial aspect of stormwater management that plays a key role in enhancing urban water sustainability. Cities must comply with strict regulations established by local and national authorities to ensure that stormwater runoff is properly managed, thereby protecting both the environment and public health.
By adopting innovative stormwater management techniques, such as green infrastructure, permeable pavement, and rain gardens, urban areas can meet these regulatory standards, reduce pollution, replenish groundwater supplies, and improve water quality. Adhering to these requirements significantly contributes to advancing urban water sustainability efforts and helps create more resilient cities for the future.
Conclusion
Effective stormwater management is crucial for improving urban water sustainability, especially given the challenges posed by increasing urbanization and climate change. By implementing innovative strategies like green infrastructure, permeable pavements, and rain gardens, cities can significantly reduce water pollution, mitigate flooding, promote groundwater recharge, and enhance climate resilience. Furthermore, viewing stormwater as a valuable resource and encouraging community involvement can strengthen urban water management systems. As cities adopt these sustainable practices, they not only comply with regulatory requirements but also lower infrastructure costs, ultimately paving the way for more resilient and environmentally friendly urban environments.